May
11th,
2017
- CREATED
Reinforcement Learning
강화학습관련 동영상 강의 요약 김성훈교수 youtube 동영상 강의 : https://hunkim.github.io/ml/
Nature of learning
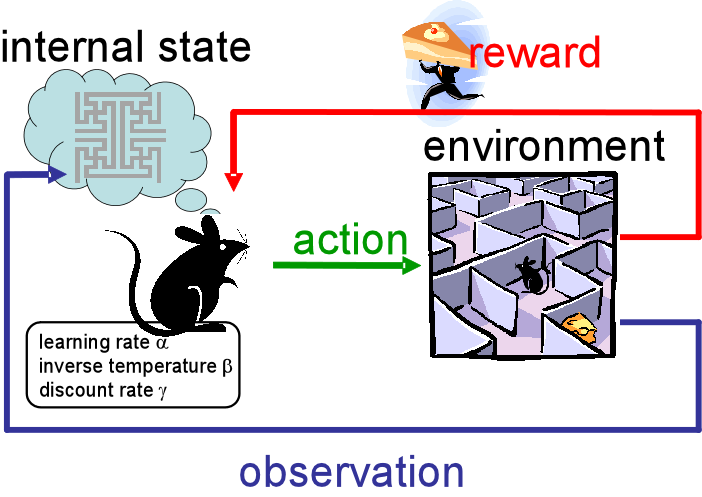
- 기본 아이디어 : 과거의 경험으로부터 학습, 상호 작용을 통한 학습
- state, actor, enviroment
- DeepMind collaborations with Google

- 활용 분야 : robotics, resource allocation, inventory management, finance
실습1, OpenAI Gym Games1, FrozenLake
- 설치 :
$ sudo apt install cmake $ sudo -H pip install gym $ sudo -H pip install gym[atari] #atari game 관련 platform - tensorflow + docker 사용
CPU 버전
$ docker pull suker/tensorflow:CPU $ docker run -d --name tenf-CPU -p 8887:8888 -p 6005:6006 -v $PWD:/notebooks -e PASSWORD=nexell suker/tensorflow:CPU $ docker exec -d tenf-CPU /run_tensorboard.shGPU 버전
$ docker pull suker/tensorflow:GPU $ nvidia-docker run -d --name tenf-GPU -p 8888:8888 -p 6006:6006 -v $PWD:/notebooks -e PASSWORD=nexell suker/tensorflow:GPU $ docker exec -d tenf-GPU /run_tensorboard.sh - test gym
class _Getch:
def __call__(self):
fd = sys.stdin.fileno()
old_settings = termios.tcgetattr(fd)
try:
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
ch = sys.stdin.read(3)
finally:
termios.tcsetattr(fd, termios.TCSADRAIN, old_settings)
return ch
inkey = _Getch()
LEFT = 0
DOWN = 1
RIGHT = 2
UP = 3
arrow_keys = {
'\x1b[A' : UP,
'\x1b[B' : DOWN,
'\x1b[C' : RIGHT,
'\x1b[D' : LEFT}
import gym
from gym.envs.registration import register
import sys,tty,termios
def gameplay() :
register(
id='FrozenLake-v3',
entry_point='gym.envs.toy_text:FrozenLakeEnv',
kwargs={'map_name' : '4x4', 'is_slippery': False}
)
env = gym.make('FrozenLake-v3')
env.render()
while True:
key = inkey()
if key not in arrow_keys.keys():
print("Game aborted!")
break
action = arrow_keys[key]
state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
print("State: ", state, "Action: ", action, "Reward: ", reward, "Info: ", info)
if done:
print("Finished with reward", reward)
break
gameplay()
Q-Learning
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vd-gmo-qO5E&feature=youtu.be
-
state + action -> Q -> quality(reward) : Q (state,action)
Q (sl, LEFT):0 Q (sl, RIGHT):0.5 Q (sl, UP):0 Q (sl, DOWN):0.3 Max Q = max Q(s,a’)
- policy : maximum value를 찾는다.
-
Q를 어떻게 학습시키는가?
Assume (believe) Q in s’ exists s상태에서 a를 수행했을때 받는 r ==> Q(s,a) = r + max Q(s’,a’ ) s0,a0,r1,s1,a1,r2,…,s n-1,a n-1,rn,sn(terminal state) R = r1+r2+r3+…+r(n) R(t) = r(t)+r(t+1)+r(t+2)+…+rn = r(t) + R(t+1) R(t)* = r(t) + maxR(t+1) optimal
-
Dummy Q-learning algorithm
각각의 s,a table을 0으로 초기화한다. 무한 반복 : action -> receive r, -> observe s’ -> update table
실습2, Q-learning(table)
import gym
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from gym.envs.registration import register
import random as pr
def rargmax(vector):
"""
vector shape [0 0 0 0]
"""
m = np.amax(vector) # vector에서 가장 큰 값을 얻어온다.
indices = np.nonzero(vector == m)[0] # m과 일치하는 vector의 index, 즉 max index
return pr.choice(indices) # m과 일치하는 vector의 index는 여러개가 있을 수 있으므로
# 그중에서 하나를 random하게 가져온다.
# gym package : 아래 소스 참고
#/usr/local/lib/python3.5/dist-packages/gym/envs/registration.py
register(
id='FrozenLake-v3',
entry_point='gym.envs.toy_text:FrozenLakeEnv',
kwargs={'map_name' : '4x4', 'is_slippery': False}
)
env = gym.make('FrozenLake-v3')
env.render()
def playgame() :
"""
Q shape [[] [] [] []
[] [] [] []
[] [] [] []
[] [] [] []]
"""
Q = np.zeros([env.observation_space.n, env.action_space.n])
num_episodes = 2000
rList = []
for i in range(num_episodes):
state = env.reset()
rAll = 0
done = False
while not done:
action = rargmax(Q[state, :])
new_state, reward, done,_ = env.step(action)
Q[state, action] = reward + np.max(Q[new_state,:])
rAll += reward
state = new_state
rList.append(rAll)
print("Success rate: %.3f"%(sum(rList)/num_episodes))
print("Final Q-Table Values")
print("LEFT DOWN RIGHT UP")
print(Q)
plt.bar(range(len(rList)), rList, color="blue")
plt.show()
playgame()